Risk and resilience in the late glacial: A case study from the western Mediterranean
Abstract
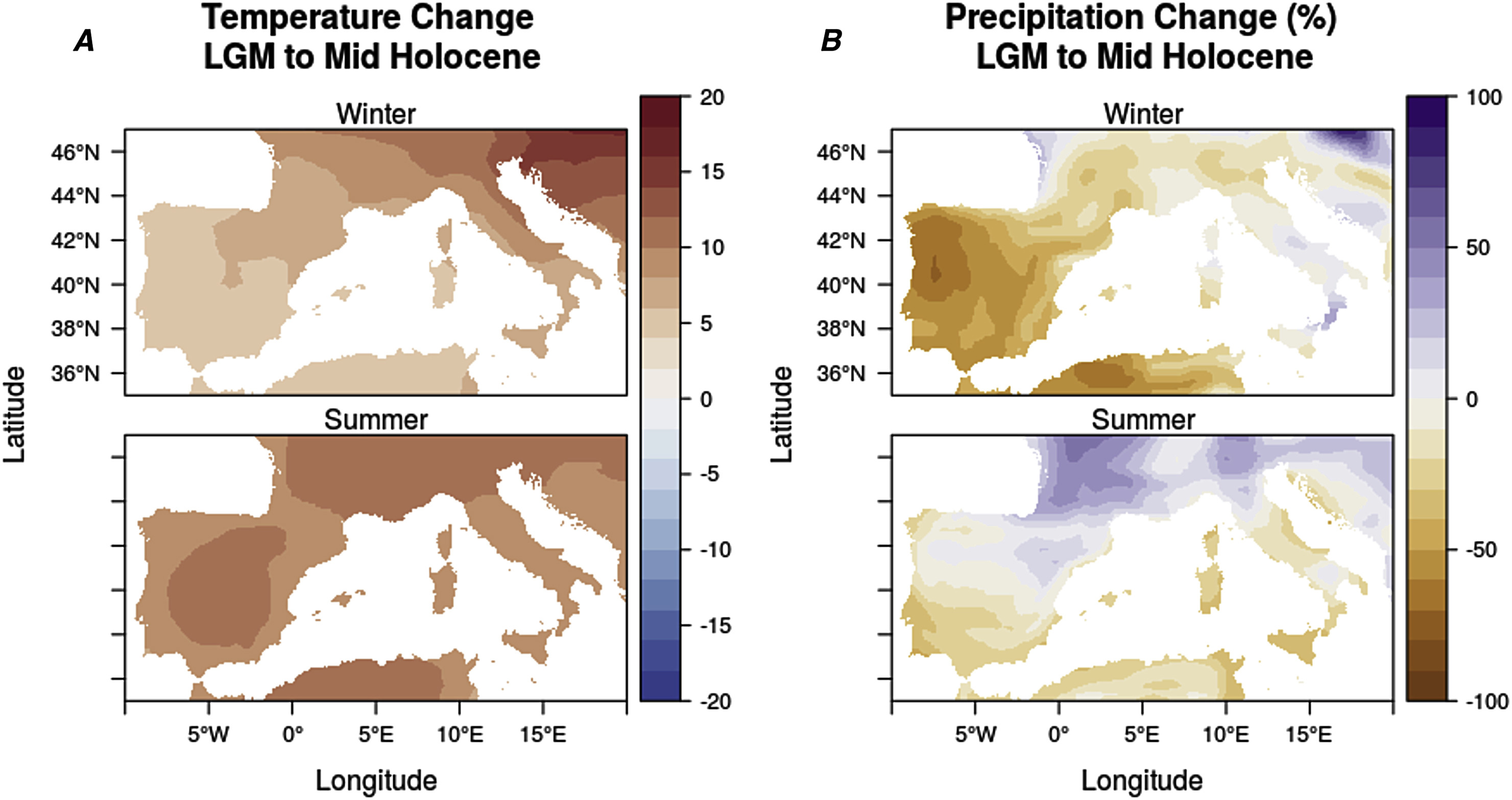
The period spanning the Last Glacial Maximum through early Holocene encompasses dramatic and rapid environmental changes that offered both increased risk and new opportunities to human populations of the Mediterranean zone. The regional effects of global climate change varied spatially with latitude, topography, and distance from a shifting coastline; and human adaptations to these changes played out at these regional scales. To better understand the spatial and temporal dynamics of climate change and human social-ecological-technological systems (or SETS) during the transition from full glacial to interglacial, we carried out a meta-analysis of archaeological and paleoenvironmental datasets across the western Mediterranean region. We compiled information on prehistoric technology, land-use, and hunting strategies from 291 archaeological assemblages, recovered from 122 sites extending from southern Spain, through Mediterranean France, to northern and peninsular Italy, as well as 2,386 radiocarbon dates from across this region. We combine these data on human ecological dynamics with paleoenvironmental information derived from global climate models, proxy data, and estimates of coastlines modeled from sea level estimates and digital terrain. The LGM represents an ecologically predictable period for over much of the western Mediterranean, while the remainder of the Pleistocene was increasingly unpredictable, making it a period of increased ecological risk for hunter-gatherers. In response to increasing spatial and temporal uncertainty, hunter-gatherers reorganized different constituents of their SETS, allowing regional populations to adapt to these conditions up to a point. Beyond this threshold, rapid environmental change resulted in significant demographic change in Mediterranean hunter-gatherer populations.